Ozone Hole Over the South Pole
Watched 1,035 times
Video description
What is Ozone Hole Over the South Pole about?
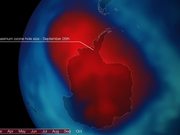
Preliminary analysis using NOAA satellite data indicates that at 18.9 million square kilometers (about 7.3 million square miles), the ozone hole over the South Pole reached its maximum annual size on September 26, 2013. Shown here is the total ozone concentration over the South Pole on September 26, 2013 using data from NOAA's Total Ozone Analysis using SBUV/2 and TOVS measurements. The "hole" is designated as the area where the total ozone concentration is below 220 Dobson units (a measure of thickness). In this animation, those values are colored red.
Can we play Ozone Hole Over the South Pole on mobile?
No, Ozone Hole Over the South Pole is designed for desktop play and works best on computers using a keyboard or mouse.
Is Ozone Hole Over the South Pole free to play?
Yes, Ozone Hole Over the South Pole is free to play on Y8 and runs directly in your browser.
Can we play Ozone Hole Over the South Pole in full screen mode?
Yes, Ozone Hole Over the South Pole can be played in full screen mode for a more immersive experience.
Added on
22 May 2016
Comments